A student posed me this question on my live chat, and what follows is a slightly more elaborated response for the purpose of sharing here.
Quite briefly, there are 2 main approaches to expanding productive capacity, with each having corresponding challenges:
1. Increase the quantity of resources
Aka increasing the long-run aggregate supply:
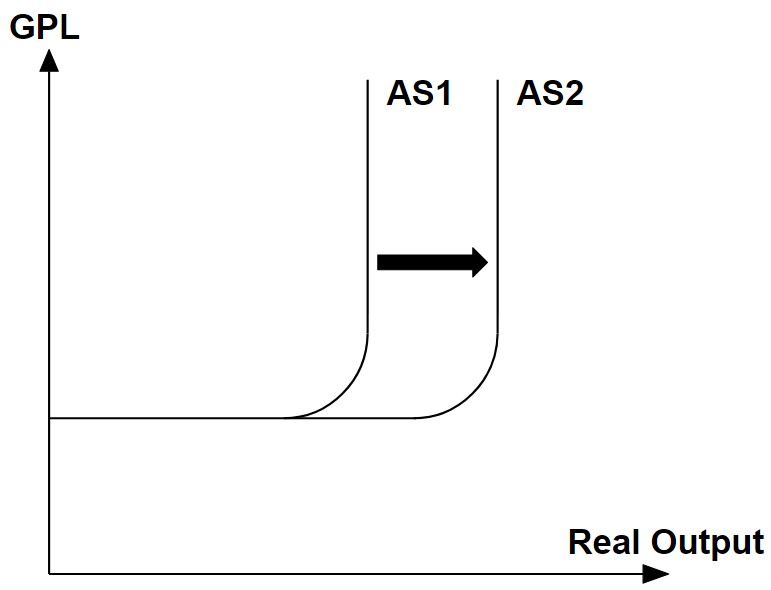
- Increase labour
- May result in strain on infrastructure such as hospitals, roads, access to food etc.
- Frequently linked to destabilising social fabrics.
- Increase capital
- Takes time to accumulate capital stock.
- Diverts resources from producing consumer goods and possibly reduces consumers’ welfare in the short-run.
- Increase land
- Part of natural endowment that may not be easy to increase or utilise further.
- Increase entrepreneurship
- Strongly dependent on the business and even cultural environment, and may not be easily improved organically.
- Improve the utilisation rate of existing factors of production (pseudo-resource increase)
- Often linked to structural deficits which need to be solved first, e.g. poor transport or education.
- Can lead to over-exploitation of resources.
2. Improve the quality of resources
Aka improving the short-run aggregate supply:
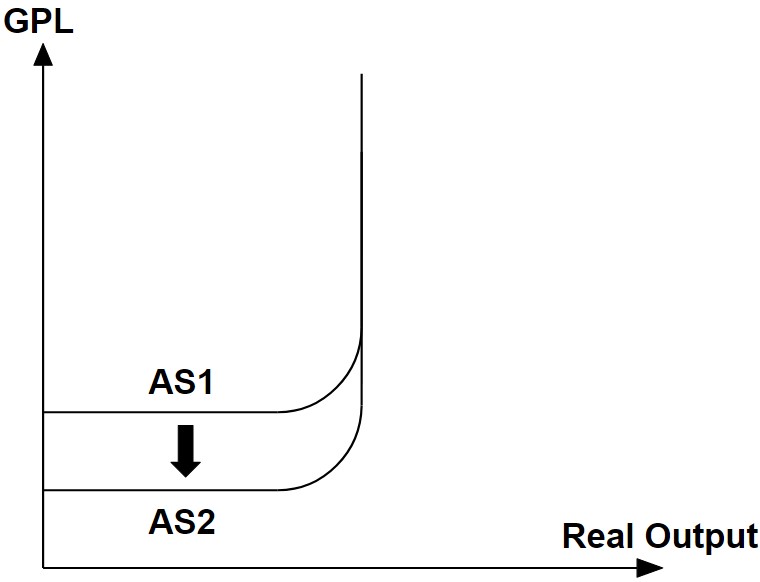
- Improve production techniques
- Organic improvements from R&D can get very expensive and risky, and may not be viable even, for less well-off countries
- Takes significant amount of time to develop
- Can result in unintended consequences (e.g. structural unemployment due to automation)
- Make better factors of production
- Can result in higher costs of production which may offset higher efficiency in production
- Also often requires time and money to develop
Other challenges in adopting supply-side policies.
- Political challenges
- Implementing supply-side policies can be difficult due to impacts to various interest that may get affected with these changes.
- Demand-limited impact
- Depending on the size of the employment state of the economy, it is possible for supply-side policies to have reduced contributions to economic growth:
- Unequal distribution of benefits
- Incoming investments frequently benefits the immediate location or industry directly, and not economy-wide.
- More generally, improvements to resources often find greater benefits with those already in position to take advantage of.
Summary
The above response was a touch-and-go explanation that does little justice to the details and nuances that should accompany a proper discourse.
Nonetheless it should be clear that supply-side policies are a broad class of policies that can be usefully dissected for analysis as I have done earlier, to suss out policy-specific difficulties.
Equally as important, the overarching theme in regards to the difficulties in executing supply-side policies most commonly have to with:
- Time
- Cost (Explicit, implicit or unintended)
If further elaboration of any of these points are needed, feel free to ask me in the comments below.
